Basic Knowledge of DWDM(Dense Wavelength Division Multiplexing)
WDM combines a series of optical signals with different information but different wavelengths and transmits them along a single fiber. WDM technology can be devided into two different type: one is CWDM and another one is DWDM. DWDM combines optical carriers on a single fiber to increase the transmission capacity of each fiber. CWDM (Sparse Wavelength Division Multiplexing) has a large wavelength interval, generally 20 nm. In contrast, DWDM (dense wavelength division multiplexing) has a smaller wavelength interval, just around 0.8-2 nm.
Structure of the DWDM
DWDM can carry SDH services, IP services, and ATM services.The ITU ITU standard DWDM wavelength is 1528.77 nm to 1563.86 nm, which has low attenuation and dispersion mainly in the C band. The 100 GHz (0.8 nm) wavelength spacing can have 40 channels, and the 50 GHz (0.4 nm) wavelength spacing can have 80 channels.
- Optical repeater: completes the conversion of wavelength light;
- Optical combiner and optical splitter: complete combining and splitting of fixed-wavelength optical signals;
- Optical amplifier (OLA): located in the middle of the optical transmission section, the optical signal is amplified by the OLA;
- Optical monitoring channel: used to carry the management and monitoring of the DWDM system, enabling the network management system to effectively manage the DWDM system.
Types of DWDM
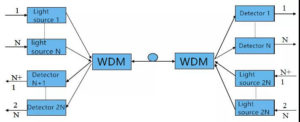
1. Double fiber one-way transmission: The unidirectional wavelength division multiplexing system uses two optical fibers, one optical fiber only transmits one direction optical signal, and the reverse optical signal transmission is completed by another optical fiber.
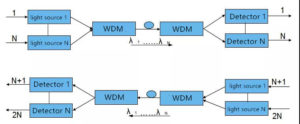
2. Single fiber bidirectional transmission: The two-way wavelength division multiplexing system only needs one fiber, and transmits it in two different directions at the same time on the fiber, and the wavelengths used are separated from each other to realize full-duplex communication with each other.
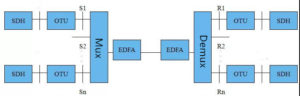
3. Open DWDM system: The OTU is used to convert non-standard wavelengths to standard wavelengths at the transmitting end. The main function of the device is to convert non-standard wavelengths into standard wavelengths specified by ITU-T to meet the wavelength compatibility of the system.
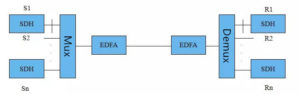
4. Integrated DWDM system: The service signal itself has already met the standard wavelength, and the OTU is not required at the receiving end.
Conclusion
DWDM technology makes full use of fiber bandwidth resources, multiplexes dozens or even hundreds of channel signals in one fiber, and the capacity of a single fiber is greatly improved. Its large-capacity and long-distance transmission characteristics have become the first choice for backbone network, core metropolitan area network, and local backbone transmission equipment.


